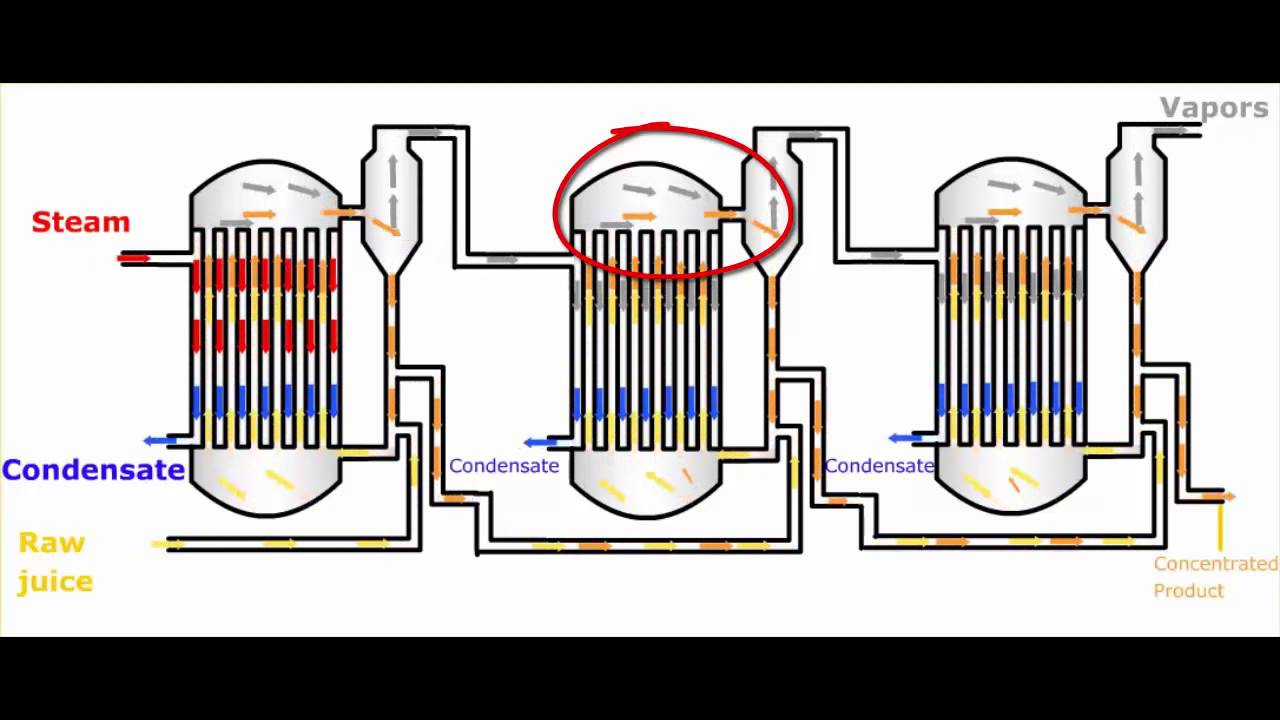
Multi-Effect Evaporator (MEE) is a critical thermal separation technology widely used in industries to concentrate solutions, recover valuable products, and minimize liquid waste. Built on the principle of using vapor from one stage as the heating medium for the next, MEE systems are known for their energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. With the increasing demand for Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems and sustainable manufacturing practices, MEE has emerged as an indispensable component in sectors like textiles, pharmaceuticals, food processing, sugar refining, and chemical manufacturing.
Unlike conventional evaporators, MEEs are custom-engineered to handle high TDS effluents, corrosive media, organic solvents, and heat-sensitive fluids, making them highly versatile. Their integration with vapor recompression, automation systems, and hybrid RO setups further enhances their operational value, offering unmatched performance with low energy footprints.
Not Just for Water Evaporation
Most people associate MEE systems with just concentrating water-based solutions, but they are also engineered to handle challenging liquids, including:
- Organic solvents (like ethanol, acetone, and isopropanol) used in pharmaceutical and fine chemical processes.
- Acidic solutions like hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid where standard materials like stainless steel may corrode. In such cases, specialized construction materials such as tantalum, Hastelloy, or glass-lined steel are used.
- Radioactive liquids in the nuclear industry are treated using MEEs under controlled and shielded environments to reduce volume before final disposal.
Key takeaway: The MEE is not limited to water-based systems. It plays a vital role in handling aggressive or sensitive fluids that need customized materials and safety protocols.
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) Backbone
MEEs are a critical component of ZLD systems, which aim to ensure no liquid waste leaves the industry. Here’s how MEE fits:
- It concentrates the wastewater up to a saturation point.
- The concentrated brine or slurry is then fed into a crystallizer or spray dryer for complete solid recovery.
- In textile dyeing, pharmaceutical API production, and tanneries, MEEs recover reusable water and reduce disposal costs of hazardous waste.
Key benefit: MEEs help companies comply with pollution norms, especially in India, where CPCB regulations are strict for industries like dyeing and electroplating.
Customized Effects for Process Fluids
In a standard MEE system, each “effect” (stage) evaporates liquid under decreasing pressure. But, in advanced systems:
- Each effect can be custom-designed based on the fluid at that stage.
- For example, in the sugar industry, the first effect handles raw sugarcane juice using high-pressure steam. The last effect is under vacuum to protect the heat-sensitive components and prevent caramelization.
- In pharmaceutical manufacturing, effects are often jacketed differently and may have unique tube materials to handle varying viscosities and corrosion levels.
Insight: Engineers select tube bundle diameter, heat transfer coefficients, and materials differently for each effect based on fluid behavior.
Use of Antiscalants and Surface Modifications
Scaling is a major issue in evaporators, especially when handling:
- High TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) water
- Calcium or silica-rich effluents
To reduce fouling: - Antiscalants like polyacrylates or phosphonates are dosed into the feedwater.
- Surface coatings like PTFE, epoxy, or glass-lining on tubes are used to minimize scale adhesion.
- In advanced systems, vibration-assisted tubes or swirling flow inserts keep the surface clean by disrupting scale formation.
Result: Less downtime, reduced cleaning frequency, and longer equipment life.
Hybrid Integration with RO Systems
Many ZLD systems use MEEs in combination with membrane systems, like Reverse Osmosis (RO). Here’s why:
- RO is cheaper for initial separation but struggles with high TDS brines.
- MEE is excellent for concentrating RO reject water.
- The hybrid approach reduces:
- Load on MEE
- Energy consumption
- Overall system CAPEX
Use case: In fertilizer industries, this combo reduces steam and chemical dosing, making operations greener and more affordable.
Multi-Effect Evaporator (MEE) technology continues to evolve as industries push for sustainable solutions in process engineering and wastewater treatment. With innovations like MVR integration, advanced automation, antiscalant usage, and industry-specific configurations, MEE systems are no longer just utility units—they are strategic assets for process optimization and regulatory compliance.
As industries worldwide transition toward resource recovery and zero-discharge goals, MEE stands at the forefront, offering a proven and adaptable solution. Whether it’s reducing environmental impact, lowering operational costs, or improving product quality, investing in an efficient MEE system is a future-ready step toward cleaner and smarter industrial operations.